Question 2:
0.2m3 of air at 4 bar and 130oC
is contained in a system. A reversible adiabatic expansion takes place till the
pressure falls to 1.02bar. The gas is then heated at constant pressure till
enthalpy increases by 72.5KJ. Calculate work done and index of expansion if the
above process is Polytrophic. Take Cp=1KJ/KgK C v=0.714KJ/Kg K..






 is defined to be:
is defined to be:
 is the work done by the system (energy exiting the system as work),
is the work done by the system (energy exiting the system as work), is the heat put into the system (heat energy entering the system),
is the heat put into the system (heat energy entering the system),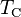 is the
is the  is the
is the 